An LED dimmer switch is a device that controls the brightness of LED lights by adjusting power to the LED driver. Unlike standard dimmers designed for incandescent bulbs, LED dimmers use trailing-edge technology to prevent flickering and buzzing. The main difference between a regular dimmer and an LED dimmer is compatibility – standard dimmers can damage LEDs or cause poor performance, while LED-specific dimmers provide smooth, flicker-free dimming from 100% down to 10% or lower.
At Votatec, we’re committed to delivering lighting solutions that make a real difference. With the rise of modern LED lighting, the way we control brightness has evolved drastically. Traditional dimmers simply don’t cut it anymore when paired with LED fixtures. If you want full control over brightness, ambiance, and energy use, understanding how an LED light dimmer works is essential. This complete guide unpacks the technology behind LED dimmer switches, why you need one (or a universal Dimmer for LED Lights), and how you can select and install the best dimmer switch for LED lights in your home or business.
What Is an LED Dimmer Switch?
An LED dimmer switch is a control device specifically built to adjust the brightness of LED lighting fixtures (including dimmable LED bulbs) by regulating power or signal to the LED driver. Since LEDs behave differently than traditional filament bulbs, a proper LED‑compatible dimmer switch is crucial.
You may also hear terms like a “dimmer switch for LED lights,” “LED brightness controller,” “low‑voltage LED dimmer” (for LED strips or low‑voltage circuits), or “smart LED dimmer” if it hooks into your home automation.
Common applications include residential lighting (living rooms, kitchens, bedrooms), commercial settings (offices, restaurants), and any space where you want fine‑tuned control rather than just on/off switching.
Why Standard Dimmers and LEDs Don’t Always Play Nice
The difference between LED technology and traditional bulbs
Traditional incandescent or halogen bulbs respond simply to reduced voltage or resistance. Dimming reduces voltage, causing the filament to glow less brightly. In contrast, LED fixtures use semiconductor chips and drivers, often operating on constant current or constant voltage. A dimmer designed for older bulbs may not interface properly with these drivers.
The issues you may face with incorrect dimmer/LED pairing
If you use a standard non‑LED dimmer with modern LED fixtures, you may experience:
- Flickering or flashing during dimming
- Audible buzzing or humming from the switch or fixture
- Limited dimming range – the light won’t go as low as you expect
- Colour shift at low brightness levels
- Shortened lifespan due to driver stress or overheating
These issues often stem from mismatched technology, inadequate minimum load capacity, or an incompatible phase‑cut method.
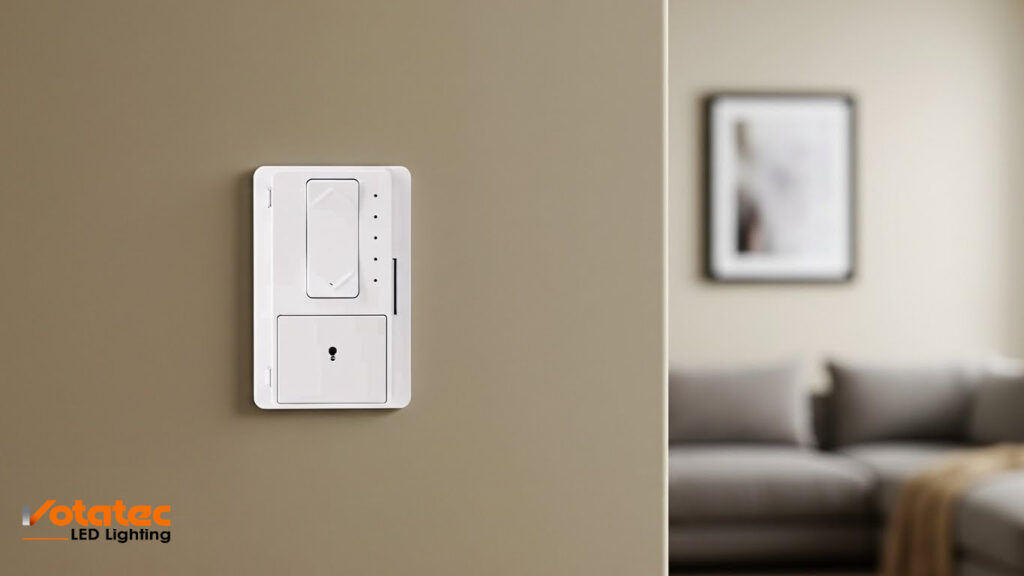

How LED Dimmer Switches Work – The Technology Behind the Scenes
Phase‑cut dimming: Leading‑edge vs Trailing‑edge
A common method for controlling brightness is phase‑cut dimming, where the dimmer chops part of each AC waveform to reduce effective power to the load.
- Leading‑edge (forward phase) dimmers: These cut the beginning portion of the AC waveform. They were originally designed for incandescent/halogen lighting and may not perform well with LED loads.
- Trailing‑edge (reverse phase) dimmers: These cut the end of the waveform, resulting in smoother control and fewer compatibility issues with LED fixtures. That’s why a trailing‑edge LED dimmer is often recommended for low‑watt LED loads.
Other dimming methods: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) & analog current control
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Rapidly switching the LED circuit on and off at high frequency so the eye perceives a continuous dimmed output. This method is especially useful for LED strips or drivers built for that control.
- Analog dimming (voltage‑ or current‑reduction): Some LED drivers reduce current or voltage rather than modulating waveform shape. If the driver isn’t designed for that method, you might get colour shifts or dimming instability.
Important electrical considerations
- Check the dimmer supports the minimum and maximum load of your LED circuit. LED loads can be very low compared to older bulb types, so an old dimmer might misbehave.
- Confirm the LED driver is labelled “dimmable” and the dimmer is marked “LED compatible.”
- Be aware of your circuit wiring: single‑pole vs multi‑way (3‑way), neutral or no‑neutral required, etc.
- If using a “universal LED dimmer,” note that while it supports multiple load types, you still need to verify compatibility with your specific LED fixtures.
- Heat and ventilation matter: if the dimmer handles many fixtures or is in a crowded box, proper thermal management is key.
Key Benefits of Using LED Dimmer Switches (and Why You Need One)
- Energy savings: Dimming reduces brightness, which means lower power consumption and less wasted heat – helping to reduce energy bills and extend fixture life.
- Enhanced ambiance & flexibility: With a smart LED dimmer or programmable LED dimmer, you can set lighting scenes, adjust for tasks (reading, relaxing, entertaining), and tailor light levels for time of day.
- Extended lifespan for fixtures: Smooth dimming reduces stress on LED drivers and lowers heat output, which can extend the lifespan of your dimmable LED bulbs and lighting system.
- Improved performance and light quality: When you pair a proper LED lighting control system with the right dimmer (like a trailing‑edge LED dimmer), you’ll see flicker‑free, quiet, smooth dimming rather than poor performance.
- Future‑proofing and smart integration: A wireless LED dimmer or smart LED dimmer switch enables remote control, voice commands and integration with your smart home ecosystem – giving you more versatility and longevity.
How to Choose the Right LED Dimmer Switch for Your Setup
Match the dimmer to your LED fixtures & load
- Verify your bulbs/fixtures are rated as dimmable LED bulbs or dimmable LED lighting – not all LED products support dimming.
- Add up the total wattage of all connected LEDs and confirm it falls within the dimmer’s capacity (both minimum and maximum).
- Choose a dimmer specifically rated for LED loads (look for labels like “LED compatible dimmer switch” or “universal LED dimmer”).
Choose the correct technology and features
- For standard household circuits with LED fixtures, opt for a trailing‑edge LED dimmer unless your drivers specify otherwise.
- If you’re dealing with low‑voltage LED strips or drivers requiring PWM, select a dimmer designed for that application.
- If you want advanced control (scheduling, scene settings, remote access), choose a smart LED dimmer switch or programmable LED dimmer.
- If you have a mixed load circuit (LED + incandescent or halogen), you might want a universal LED dimmer, but still verify actual compatibility.
Wiring & installation considerations
- Check if the switch box has a neutral wire – some smart or wireless LED dimmers require it.
- Determine if your switch circuit is single‑pole, multi‑way (3‑way) or more, and pick a dimmer rated accordingly.
- Be mindful of load distribution and heat: too many fixtures on one dimmer can overload or overheat it.
Read more: How to Install a Dimmer Switch
Tips for avoiding common mistakes
- Don’t use a dimmer with non‑dimmable LED bulbs – performance will suffer and you may damage the driver.
- Avoid using an older incandescent‑only dimmer with LED circuits unless it specifically supports LED loads.
- Check that your total load is above the dimmer’s minimum requirement – some modern dimmers require a certain load to regulate properly.
- Always test your lighting setup before finalizing: check full dimming range, ensure no flicker or colour shift, and confirm proper operation.
Installation & Best Practices for Smooth Operation
- Turn off power: Always switch off the appropriate circuit at your breaker panel before working on wiring.
- Remove existing switch: Carefully remove the old switch, note the feed (line) wire, load wire, ground and neutral if present.
- Install the new dimmer: Follow manufacturer instructions. Typically: black (line), red or coloured (load), green (ground), and neutral if required.
- Mount properly & ensure ventilation: Make sure the switch box isn’t overcrowded and the dimmer has sufficient space to dissipate heat.
- Test dimming range: After installation, gradually adjust from full brightness down to minimum and observe: no flicker, no buzzing, stable colour.
- Label your setup: It’s helpful to mark on the breaker or label the circuit that a “LED‑compatible dimmer” has been installed so future users/technicians know.
- Post‑install checks: If you later add more fixtures or change bulb types, re‑check compatibility. Don’t assume the original dimmer will remain optimal.
Common Troubleshooting & How to Fix Issues
- Flickering at low dim levels → Often means dimmer and LED driver aren’t compatible, or the load is below the minimum requirement. Solve by using an LED‑rated dimmer or increasing load.
- Buzzing or humming → Usually due to using a leading‑edge dimmer with LED load, or a low‑quality switch. Replace with a model designed for LED loads (often trailing‐edge).
- Lights won’t dim very low / stuck at a higher brightness level → The driver or dimmer may not support deep dimming. Upgrade to a dimmer or driver rated for that.
- Colour shift when dimming → The LED driver might not maintain colour temperature at low levels. Use high‑quality dimmable LED bulbs and a compatible dimmer.
- Dimmer feels hot or warm to the touch → Load may exceed the dimmer’s rating, or the box lacks ventilation. Check wiring and load, reduce fixtures, or upgrade dimmer capacity.
Case Study / Example Applications
- Residential lighting upgrade: A homeowner replaces standard incandescent downlights with dimmable LED fixtures and discovers the existing dimmer causes buzzing and flicker at low levels. After installing a proper LED‑compatible dimmer (trailing‑edge type) rated for low‑watt LED loads, the system now supports smooth dimming from 100% down to ~5% with no flicker – improving comfort and ambiance.
- Commercial hospitality setting: A restaurant integrates a wireless LED dimmer and smart LED dimmer switches to manage dining‑area lighting. By dimming during off‑peak hours, they reduce energy use, extend fixture life and deliver better mood lighting for guests. They also integrate this with an LED lighting control system for different scenes (e.g., lunch, dinner, events).
- In both examples, choosing the right dimmer switch for LED lights – paired with appropriate fixtures and drivers – delivered improved performance, control and longevity.
Future Trends in Dimmer for LED Lights
- Smart dimmers with built‑in sensors (occupancy, daylight, presence) will become more common – taking lighting control beyond just brightness adjustment to automated responsiveness.
- Voice control and full home‑automation integration (smart LED dimmer switch) will be standard in upcoming residential and commercial builds – enabling lighting scenes, remote control and enhanced flexibility.
- LED drivers and dimmers will support ultra‑low minimum loads and smoother dimming curves (down to 1% or lower) with minimal flicker or colour shift – enabling very fine control of dimmable LED bulbs.
- Building automation systems (BMS) will further integrate LED lighting control systems as part of sensor networks – allowing scene control, group dimming, energy monitoring and analytics across entire buildings.
- Regulatory standards will push for better compatibility, lower minimum loads, less flicker and more rigorous certification of “LED‑compatible dimmer” devices – making selection easier and performance more reliable.
FAQs about Dimmer for LED Lights
Can I use my existing dimmer switch with LED lights?
Only if your current dimmer is rated for LED loads (low‑wattage) and supports the correct dimming technology (often trailing‑edge). Many older incandescent‑style dimmers aren’t suitable and may cause flickering, limited dimming or shortened fixture life.
Why do my LED lights flicker when I dim them?
Flicker commonly arises from incompatible dimmer/LED driver combinations, loads below the dimmer’s minimum requirement, or using a leading‑edge dimmer when the driver expects trailing‑edge or PWM control.
What is the difference between leading‑edge and trailing‑edge dimmers for LEDs?
Leading‑edge dimmers cut the start of each AC waveform cycle and were originally designed for incandescent loads; they often cause instability with LEDs. Trailing‑edge dimmers cut the end of the waveform and are gentler on LED drivers, making them better suited for dimmable LED fixtures.
Will dimming LED lights save me money on my energy bill?
Yes. Dimming reduces brightness which in turn reduces power consumption and heat output. Over time this leads to lower energy costs and can extend the lifespan of your dimmable LED bulbs and fixtures.
How low can I safely dim an LED and still maintain good light quality?
That depends on the quality of both your LED driver and dimmer switch. With a properly matched system (LED‑compatible dimmer switch + high‑quality dimmable LED bulbs) you can often dim down to ~5% or even lower with minimal colour shift and no flicker. But mismatched components may limit performance.
Summary & Final Thoughts
At Votatec, we understand that perfect lighting isn’t just about brightness – it’s about control, ambiance and longevity. Using the correct LED dimmer switch is more than a nice upgrade – it’s essential to ensure your LED lighting performs smoothly, yields energy savings and delivers optimal comfort. Whether you’re installing a simple low‑voltage LED dimmer or a comprehensive wireless LED lighting control system with smart features, the key lies in compatibility: the LED driver, fixture, dimmer (whether a trailing‑edge LED dimmer, smart LED dimmer, or universal LED dimmer) and wiring all must work in harmony.
Take a moment to review your current setup. Choose a dimmer labelled as LED‑compatible, select the features that fit your application, and install it with care. The payoff? Flicker‑free, cool‑running, colour‑stable lighting that elevates your space and extends fixture life. And when you’re ready for that upgrade – Votatec is here to support you every step of the way.